In this blog post we will cover how to configure Red Hat OpenShift to forward logs from the ClusterLogging instance to an external 3rd party system, in this case, VMware vRealize Log Insight Cloud.
Architecture
The Openshift Cluster Logging will have to be configured for accessing the logs and forwarding to 3rd party logging tools. You can deploy the full suite;
- Visualization: Kibana
- Collection: FluentD
- Log Store: Elasticsearch
- Curation: Curator
However, to ship the logs to an external system, you will only need to configure the FluentD service.
To forward the logs from the internal trusted services, we will use the new Log Forwarding API, which is GA in OpenShift 4.6 and later (it was a tech preview in earlier releases, and the configuration YAMLs are slightly different, so read the relevant documentation version).
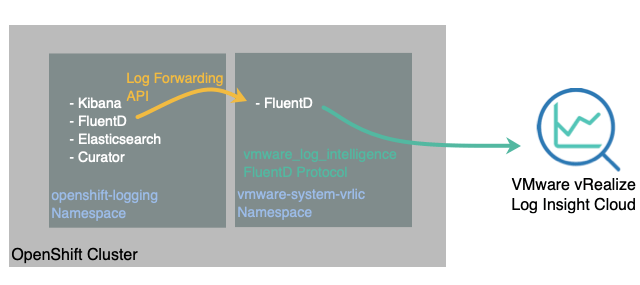
This setup will provide us the architecture below. We will deploy the trusted namespace “OpenShift-Logging” and use the Operator to provide a Log Forwarding API configuration which sends the logs to a 3rd party service.
For vRealize Log Insight Cloud, we will run a standalone FluentD instance inside of the cluster to forward to the cloud service.
The log types are one of the following:
application. Container logs generated by user applications running in the cluster, except infrastructure container applications.infrastructure. Container logs from pods that run in theopenshift*,kube*, ordefaultprojects and journal logs sourced from node file system.audit. Logs generated by the node audit system (auditd) and the audit logs from the Kubernetes API server and the OpenShift API server.
Prerequisites
- VMware vRealize Log Insight Cloud instance setup with Administrator access.
- Red Hat OpenShift Cluster deployed
- with outbound connectivity for containers
- Download this Github Repository for the configuration files
git clone https://github.com/saintdle/openshift_vrealize_loginsight_cloud.git
Deploy the standalone FluentD instance to forward logs to vRealize Log Insight Cloud
As per the above diagram, we’ll create a namespace and deploy a FluentD service inside the cluster, this will handle the logs forwarded from the OpenShift Logging instance and send the to the Log Insight Cloud instance.
Creating a vRealize Log Insight Cloud API Key
First, we will create an API key for sending data to our cloud instance.
- Expand Configuration on the left-hand navigation pane
- Select “API Keys”
- Click the “New API Key” button
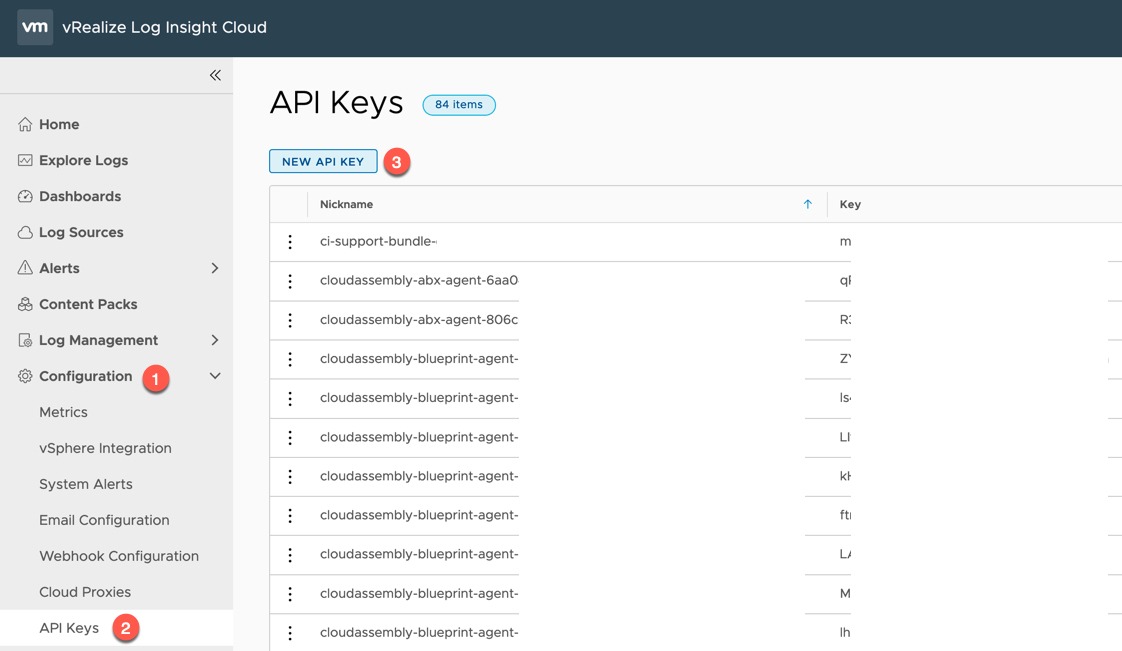
Give your API key a suitable name and click Create.