In this blog post I’m going to dive into how you can create a Tanzu Kubernetes Grid cluster and specify your own container network interface, for example, Cilium. Expanding on the installation, I’ll also cover installing a load balancer service, deploying a demo app, and showing some of the observability feature as well.
What is Cilium?
Cilium is an open source software for providing, securing and observing network connectivity between container workloads - cloud native, and fueled by the revolutionary Kernel technology eBPF
Let’s unpack that from the official website marketing tag line.
Cilium is a container network interface for Kubernetes and other container platforms (apparently there are others still out there!), which provides the cluster networking functionality. It goes one step further than other CNIs commonly used, by using a Linux Kernel software technology called eBPF, and allows for the insertion of security, visibility, and networking control logic into the Linux kernel of your container nodes.
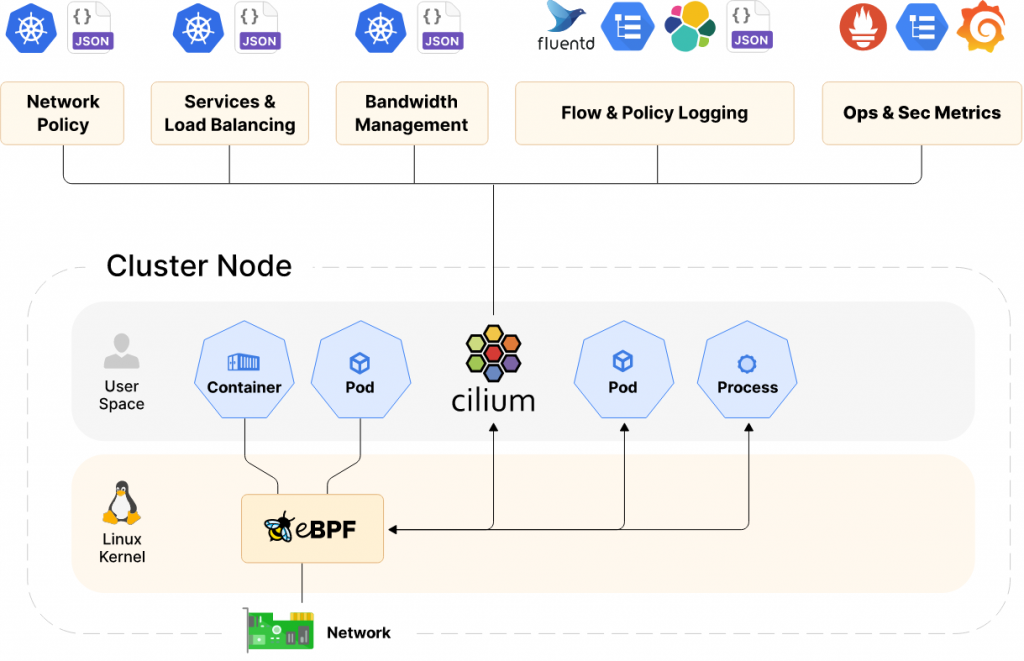
Below is a high-level overview of the features.
And a high-level architecture overview.
Is it supported to run Cilium in Tanzu Kubernetes cluster?
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid allows you to bring your own Kubernetes CNI to the cluster as part of the Cluster bring-up. You will be required to take extra steps to build a cluster during this type of deployment, as described below in this blog post.
As for support for a CNI outside of Calico and Antrea, you as the customer/consumer must provide that. If you are using Cilium for example, then you can gain enterprise level support for the CNI, from the likes of Isovalent.
Recording
How to deploy a Tanzu Kubernete Cluster with Cilium
Before we get started, we need to download the Cilium CLI tool, which is used to install Cilium into our cluster.
The below command downloads and installs the latest stable version to your /usr/local/bin location. You can find more options here. Continue reading How to Deploy a Tanzu Kubernetes Grid cluster using the Cilium CNI