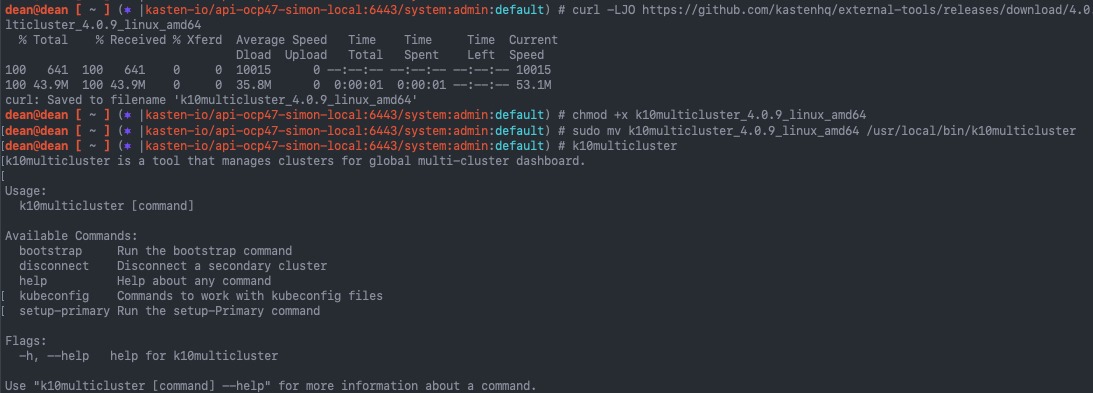
This blog post will cover deploying the infrastructure and components for Data Management for VMware Tanzu.
My second blog post will cover using this infrastructure for Self-Service Database-as-a-Service.
What is Data Management for VMware Tanzu?
Data Management for VMware Tanzu (DMS) is a newly released solution from VMware (July 2021) providing data-as-a-service toolkit for on-demand provisioning & automated management of MySQL and PostreSQL databases on vSphere platforms.
DMS is accessible as both a Graphical UI and via REST API, to meet the needs of administrators and developers and their consumption needs.
With DMS, it provides the ability to create and manage data services through a centralized platform in a self-service fashion, with the following features:
- Simplified management for admins, acting as a Database fleet management tool; presenting a view of the organization’s database instances running on multi-cloud infrastructure.
- Database users have the ability to consume self-service capabilities to create new database instances, or to operate on existing instances safely and securely, without requiring infrastructure or database expertise.
- DMS also provides full automation for provisioning data service instances, backups, security patches, and periodic updates of the data service engine.
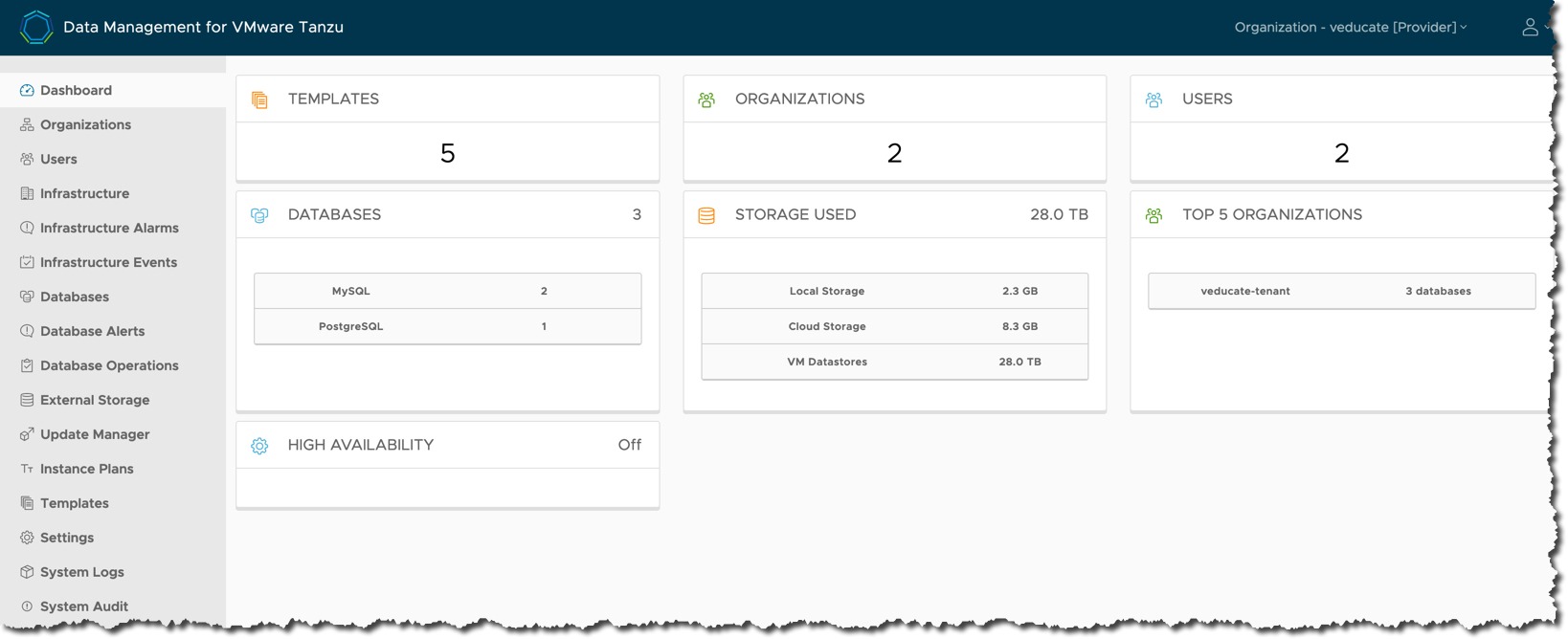
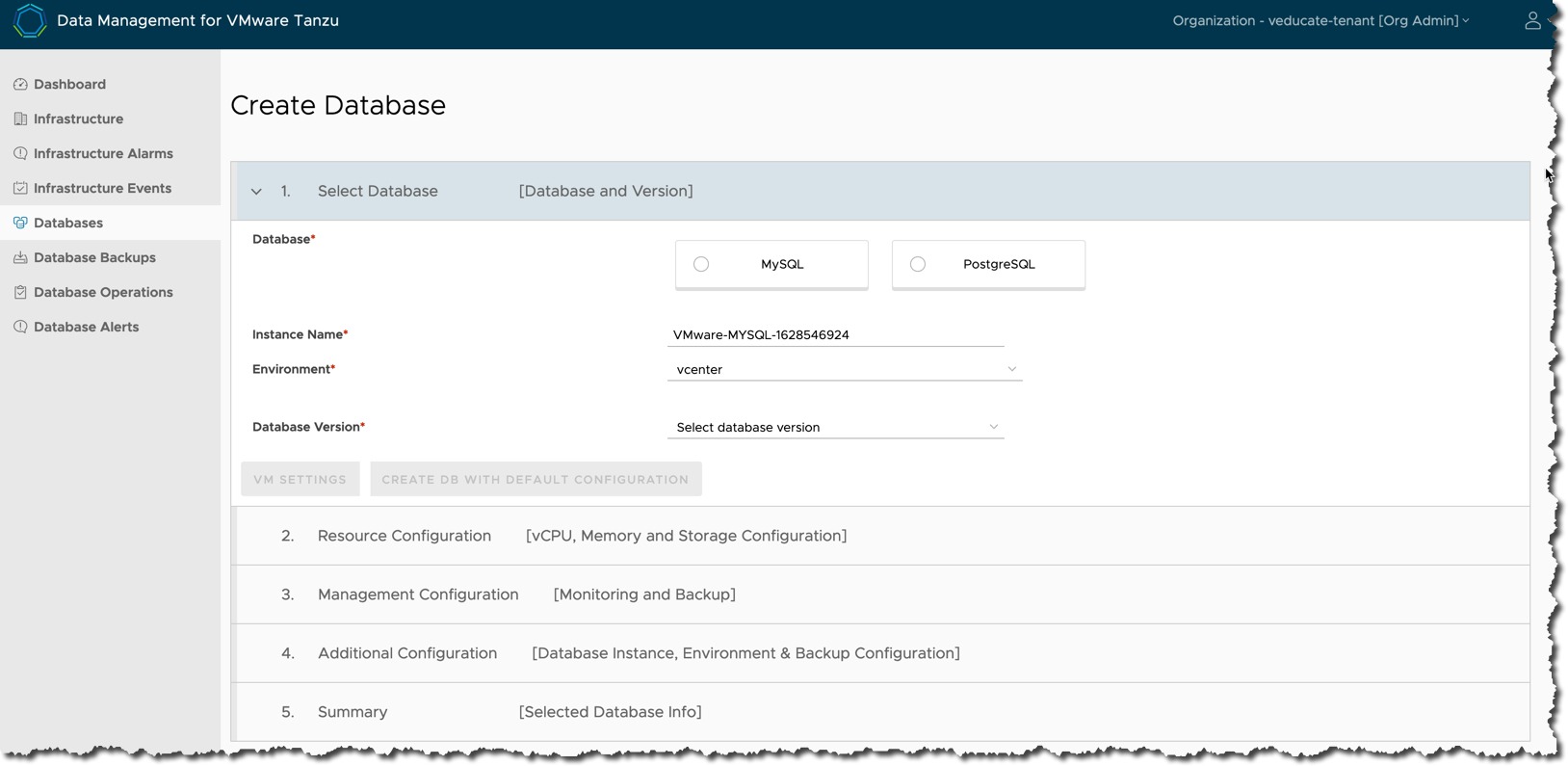
Understanding the components
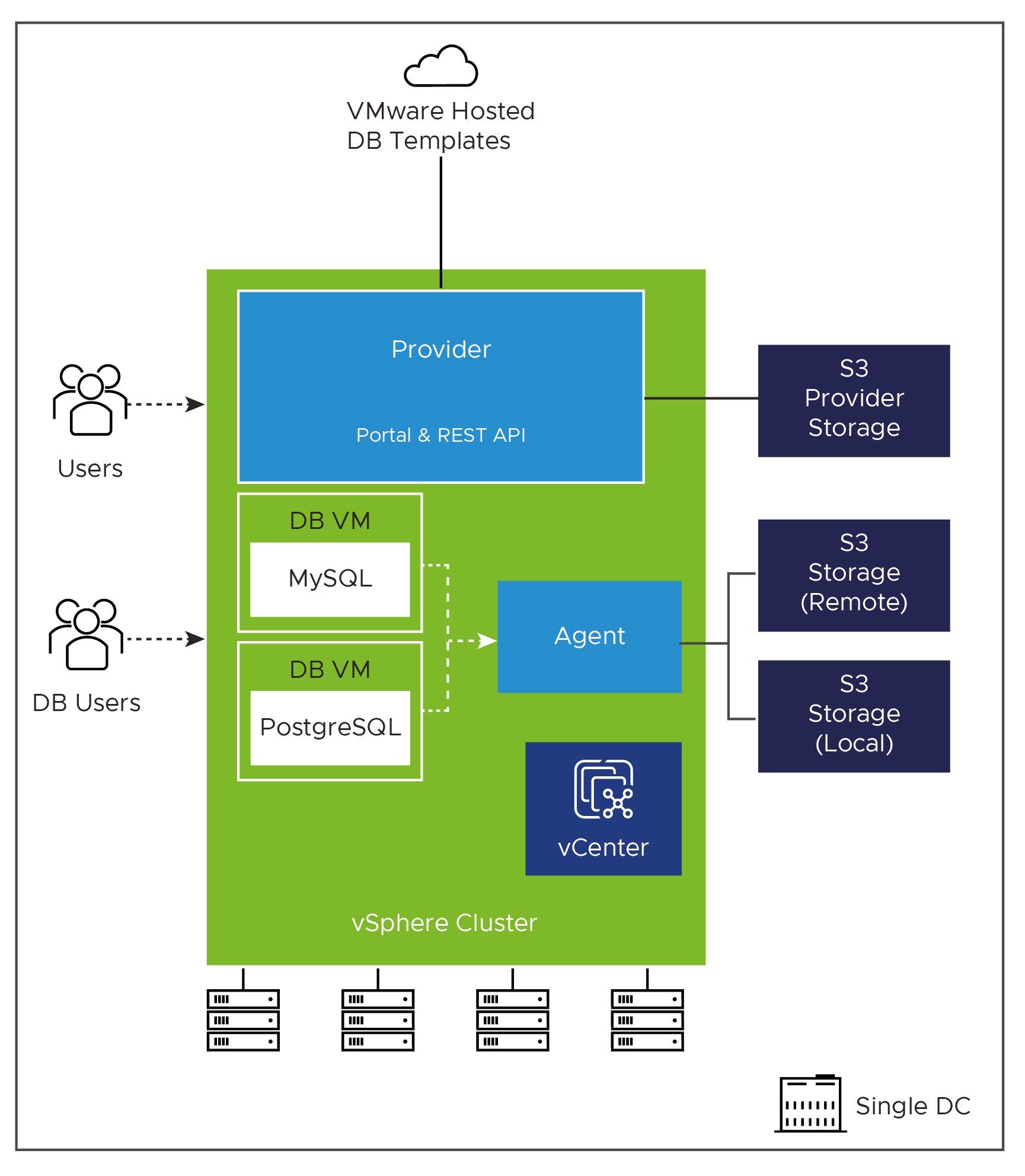
DMS is made up of the following architectural components:
- Provider – this is the core appliance you will deploy, which offers the central UI and API for all users to interact with the Data services and functions. It acts as the control plane to the other components.
- Agent – These appliances are deployed to extend the control plan into the various vSphere environments, providing a point of presence for provisioning and management operations of the Services deployed.
- Service – These are photon appliances which host the deployed instance of the data service (database). They communicate with the Agent that deployed them, via a private API. DMS supports the deployment of MySQL and PostgreSQL currently.
- Template Repo – publishes a set of Data Management for VMware Tanzu Database Templates on Tanzu Network. The provider will poll the Tanzu Network periodically for new templates. There is also a method to handle air-gap environments.
S3 storage is required to be used for several items such as location to store the templates, database configurations and database backups.
Full deployment models for the components can be found here.
Understanding Organisations and User Access
DMS implements the concept of Organisations to provide a logical grouping of users. There are two types:
- Provider Org – A type of organization to which one or more Provider Administrator user belongs.
- One provider org can exist in a single DMS installation.
- This is automatically created during the deployment of the Provider Appliance
- The Provider Org name is the company name specified at deployment.
- Agent Org – A type of organization with one or more Organization Administrator or Organization User members.
- These orgs are created via the DMS UI/API once the Provider appliance has been deployed and can be created at any time.
DMS pre-defines these three user roles:
- Provider Administrator
- This is the single Provider Role in the installation
- Among other tasks, users in this role can import additional Provider Administrator users, create organizations, and create and import organization users
- Organization Administrator
- Organization User
The Provider Administrator user will assign a role to each DMS user that they create or import in an organization.
A user that is assigned the Organization Administrator role can manage all services in the organization to which they belong. A user assigned the Organization User can manage only the services that they provision.
More detailed information on the User roles and responsibilities can be found here.
Getting Started
Now first and foremost, I’ll point you towards the official documentation to use as a reference to review alongside this blog post.
Prerequisites
There are always several things to get sorted before you ever dive right in! The official requirements are detailed here, I’m going to call out some of the more finicky pieces you need to be aware of. Continue reading Data Management for VMware Tanzu – Getting Started →